The University of Baghdad keeps pace with international development in the field of sustainable environment. It further responds to any change in international standards and requirements by relying on a flexible policy that could be adjusted accordingly. The university is aware of its responsibility towards the environmental effects of its activities. It also desires to develop a better environment for future generations; accordingly, particular goals have been set to organize the environment-protection procedures and mitigate the impacts of such activities. Such steps help ultimately build a university atmosphere that is environment-friendly and that suits meeting particular standards as the following:
The policy adopted by the university to improve the university environment includes studying the strengths and weaknesses of the university environment according to the mentioned axes to compare the progress achieved. The year 2017 has been adopted as a basis for measuring achievement rates and potential challenges. This is because the data for this year require documenting the procedures followed by the university for most of the paragraphs. This further requires conducting true and realistic measures on the part of the university administration, faculty, staff, and students. The convergence of these efforts will lead to the sustainability of the university’s environmental resources, keeping pace with modern developments, and increasing environmental awareness among the university community. This requires the provision of an accurate database on all items related to the university environment and its sustainability.
Track OneSolid and Toxic Waste Management
Waste treatment and recycling activities are among the main factors in creating a sustainable environment due to the large number of wastes that is produced on campus. Accordingly, waste treatment programs must be among the university interests, thus, the university recommends:
- Collecting data related to the quantity and type of solid and toxic waste generated on campus.
- establishing organic and inorganic waste sorting projects and benefiting from them
- Forming teams of volunteers (students, staff and faculty members) to assist in the waste management plan
- Activating the tasks of environment-friendly committees
- Building and developing the capabilities of university staff, who are especially located in the Diwan Affairs Department, in the field of integrated waste management
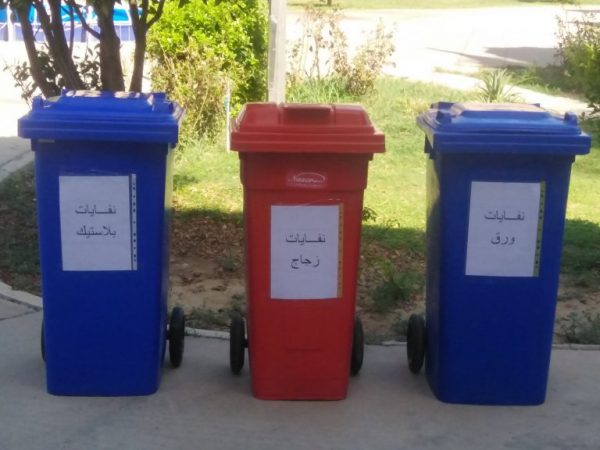
- Educating employees and students about the use of an official policy for dealing with paper and plastic, such as (placing guiding advertisements to rationalize the use of paper to reduce consumption, and raising awareness on the harms of using plastic and paper cups, etc.)
- Cooperating with the Diwan Affairs Department in preparing containers of different colors (blue, red, yellow, green) to help in the waste sorting process, and to develop a program that treats a specific part of the waste
- Activating the mechanism for storing and disposing of toxic waste by applying waste sorting technique with the help of the relevant authorities inside and outside the university
- Recycling wastewater in cooperation with the relevant authorities and finding solutions to benefit from it.
- Maximizing the university resources by benefiting from solid waste revenues (paper, cardboard, metal and plastic cans, etc.).

One of the important projects in this pivot is the project to produce environmentally friendly, biological, and organic fertilizers.
This project aims to produce environmentally friendly nitrogen, phosphate and potassium fertilizers from university animals and plants’ wastes after converting them into organic and biological fertilizers. The project is educational and training, especially for postgraduate students. It encourages them to do such projects after graduation. Different species of bacteria and fungi are used in the production of biofertilizers, such as Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Blue green algae, and Mycorrhiza
One of the projects to produce environmentally friendly organic fertilizers and the treatment of agricultural wastes is the production of organic fertilizers from the residues of the Conocarpus plants to be used later in the growth and production of horticultural plants. Such organic fertilizers are good and free of chemical additives that raise the level of salts in the soil. They also improve the quality of the agricultural product by reducing the level of nitrates that negatively affect human health. Finally, they benefit from the pruning residues of these trees and limit the growth of their roots.
Track TwoEnergy Management
Our university is expected to increase great efforts in raising energy efficiency in its buildings and in taking more care of nature and energy resources using energy-saving devices, the adaptation to climate change, or through adopting the policy of using renewable energy, energy conservation program, green buildings, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be met through:
- Using modern methods to conserve energy
- Using modern methods for smart buildings through the installation of sensors for water taps, self-extinguishing of lighting, etc.
- Determining the types of energy used in the university
- Specifying the amount of electrical energy consumption
- Establishing green buildings
- Using clean energy
- Measuring carbon dioxide emissions (Co2).
Therefore, the university recommends for improvement the following:
- Implementing procedures to ensure energy efficiency in all new projects and buildings.
- Gradually applying energy efficiency standards in existing buildings by directing procurement committees to provide economic equipment.
- Working with academics to use their expertise to solve problems and implement effective solutions.
- Raising the awareness of students and employees and holding workshops to train them.
- Installing sub-meters for faculties to measure energy use and determine consumption and saving points.
- Directing the Construction and Projects Department to prepare a study on the consumption of electric energy in the university formations and on the transition to alternative energy.
- Installing meters to measure the electrical energy consumption of each formation in the Jadiriya campus in detail.
- Rewarding the formation that uses modern means to reduce the consumption of electrical energy and alternative energy sources
- Developing and implementing a plan for the use of environmentally friendly modes of transport
- Developing a roadmap for reducing carbon emissions.
- Working with the central cooling and heating system due to its impact on reducing the consumption of electrical energy and preserving the environment.
Among the most important projects that the University of Baghdad is interested in within the field of renewable energy are:
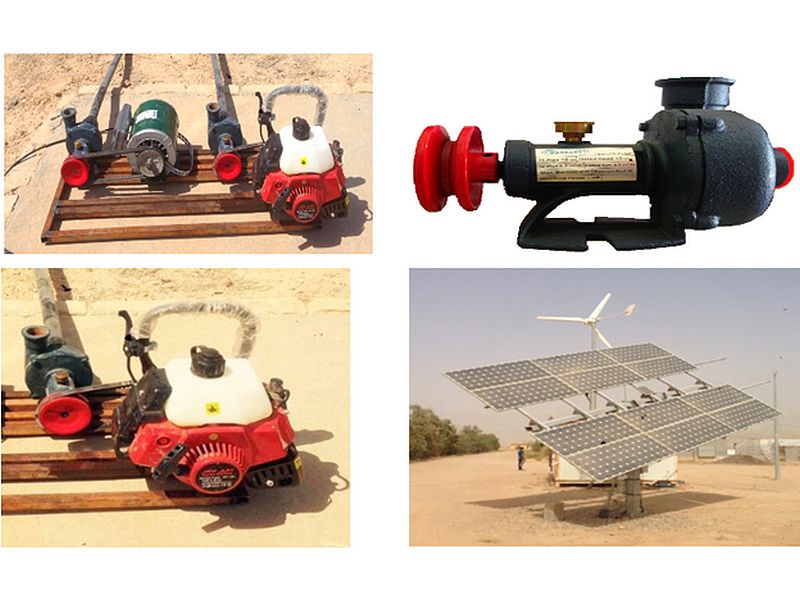
Manufacturing and assembling a pumping unit with a motor operating with four sources of energy used in irrigation
The study of operating costs of agricultural equipment and pumps aims to obtain high operating efficiency and productivity at the lowest possible costs. Pumping systems that operate on diesel fuel need to calculate fuel and maintenance costs. By increasing the load on the diesel engine, fuel and maintenance costs increase. On the contrary, renewable energy systems represented by solar energy and wind energy do not need continuous maintenance. This makes it most suitable for remote areas that are far from electricity supply centers, where technicians are not available to maintain and repair diesel engines. In addition to the above, they are clean and environmentally friendly energy.
In order not to give an opportunity for the reluctance of farmers to operate the pumping unit in the drip or sprinkler irrigation systems in the desert areas when there is no national electricity, or where there is a lack of fuel, it has been found necessary to think about finding energy alternatives. The latter are called renewable energy; it provides arable land in remote areas and far from sources with electricity, providing as a result job opportunities and increasing local production.

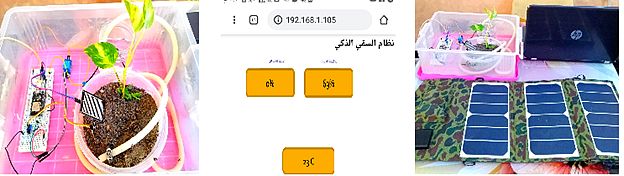
A smart irrigation system using the internet of things and solar energy
This project proposes a smart irrigation system using the Internet of Things that can be used to control the watering of plants. The level of water in the soil is detected using either a soil moisture sensor type with measurement of humidity or ambient temperature in order to track the early signs of changes in temperature. These sensors are connected to a Wi-Fi board. The collected data is then uploaded to the cloud (esp32.com) and displayed through an application or website. Notifications are constantly sent to the user to make the system easy to use
The project further relies on the solar energy system as a clean and sustainable energy source. It avoids pollution resulting from the use of diesel pumps or other forms of energy, reduces waste of water, and preserves water resources from the misuse of plant irrigation so that the process is fully automated and intelligent via the Internet. The system controls the process of watering plants automatically, as it reduces the need for human intervention to a large extent. The system contributes to saving time, reducing costs, protecting the environment, reducing maintenance, operation costs, and effective irrigation service..
Track ThreeUniversity Infrastructures
This hub shows whether a campus is worth a college campus. The aim is to get the university to participate in providing more space for green spaces and environmental protection, in addition to energy development
Such a procedure requires determining the locations of the university, its college areas, buildings, green spaces, unexploited places, and infrastructure, click here.
Track FourWater Management
The university aims to reduce water use by developing a water conservation and piped water use program. Such a procedure helps to preserve water by raising its use and management efficiency through the following:
- Adopting water conservation policy within the university
- Adopting a program that helps to recycle water inside the university
- Applying systems that reduce water consumption
- Determining the amount of water that is saved and treated
Therefore, the university recommends improving water management through:
- Encouraging university formations to rationalize water use and increase conservation programs.
- Providing programs for water recycling and for using treated water when watering plants
- Developing a policy for collecting water from air-conditioners and using it to irrigate plants.
- Using faucets equipped with automatic sensors to significantly reduce water consumption.
- Implementing awareness and coordination programs to raise the efficiency of water use and encourage students and employees to rationalize water consumption.

The total area of the water surface of the university (water channels around the university, artificial lakes, sedimentation basins, fountains, and swimming pools) is about 17,680 square meters.
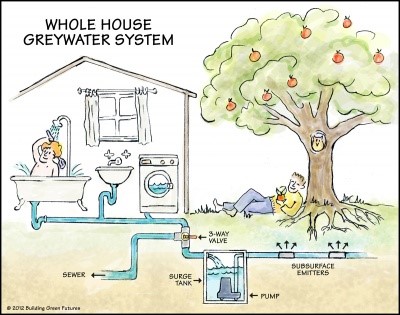
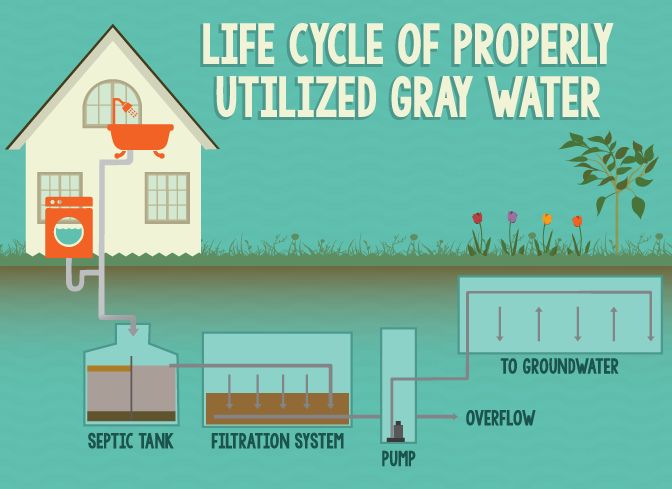
One of the projects adopted by the university is the project of reusing treated gray water to increase available water, get rid of gray water, and reduce environmental pollution, which relieves pressure on fresh water.
Gray water is the water that comes out of sinks, bathtubs, showers, washing machines, and floor drains. Although this water is no longer clean, the percentage of its contamination is much lower than that of sanitation water. From here came the idea of reusing it, as gray water that can be treated relatively easily and at the same site of its production. Then, this water can be reused as a new water source from non-traditional water sources used to irrigate agricultural crops and plants grown in homes, public gardens, parks, etc. It further helps to increase irrigated land areas, food security, and environmental protection from pollution caused by gray water if it is disposed of improperly. It also works to protect the environment in general from pollution resulting from the overflow of cesspits or their emptying in valleys and public streets, as well as protecting ground and surface water sources.
Processing Methods:
Treatment units can be established in homes, villages, rural areas, gardens, public parks, schools, universities, and other civil buildings for the purpose of irrigation. The use of gray water is not limited to irrigating plants. For example, gray water is used in some countries to wash sanitary facilities. The gray water treatment units aim at:
- Reducing the use of fresh water costs the consumer a sum of money that must be paid to get water and a new water source at a low price.
- Reducing the cost of the water production unit, as many water consumers depend on drilling wells, which cost a lot of money.
- Reducing the expenses of disposing of gray water that pollutes the environment. This is because many small population centers do not have public sewage networks; a matter which makes the people compensate for that by making cesspits, which often have many disadvantages as they need to be emptied continuously. This is considered somewhat expensive due to the high cost of emptying; therefore, most families leave these pits to fill up, creating as a result a health problem for everyone due to the smells, insects, and diseases. In large cities, there are public sewage networks that they also suffer from many problems because of the age of these networks that need to be checked and maintained regularly.
- The use of appropriately treated wastewater helps dispense with some fertilizers that cost a lot of money. This is because they contain organic matter and some nutrients needed for crops.

Track FiveTransportation and Roads Management
The transportation system plays an important role in the level of carbon emissions and pollutants in the university. The use of buses and bicycles on campus will negatively affect the university environment. Thus, transportation policy must be amended to reduce the number of motorized vehicles on campus, to encourage students and employees’ movement behavior on foot when walking around on campus, and to avoid using private vehicles. The use of environmentally friendly public transportation will reduce the carbon footprint around the campus.
Therefore, the university recommends an improvement in the transfer policy through:
- Introducing the issue of on-campus transportation for investment by preparing an economic feasibility study on the actual reality of on-campus transportation in terms of environmental damage and high maintenance costs.
- Educating members to adopt the sport of walking to move around the university campus to reduce the use of private cars, and the use of bicycles instead.
- Putting a road map for cars, pedestrians, and bicycles in the form of guiding signs in the designated places within the university campus.
- Setting a university transportation policy (such as car sharing and bicycle sharing).
- Adopting future projects that serve the university in cooperation with the relevant authorities (the Baghdad Municipality, the Baghdad Provincial Council), for example (the metro/ tram).
Track SixResearch and Education
This track is considered one of the most important axes, as it gives the university an important role in creating the interest of the new generation in sustainability. Therefore, the university recommends developing this pivot through:
- Increasing study contents related to the environment and sustainability and encouraging scientific research.
- Encouraging volunteer work and creating forums and activities for students.
- Increasing the number of courses, workshops and seminars related to the environment and sustainability.
- Setting a budget for the environment and sustainability within the university budget.
- Specifying a site for environment and sustainability that is concerned with special activities, such as research, panel discussions, publishing lectures, volunteer work for students, etc., which are practiced by the various formations of the university.
- Implementing the standard specification for social responsibility (26001).
Track SevenClimate Change
Climate change is a boundless global challenge and combat. It requires coordinated action by all countries. The main cause of climate change is global warming, which has many negative effects on the physical, biological, and human systems, as well as other impacts. As global warming is caused by the greenhouse effect, which is a natural process in which the atmosphere retains some of the sun’s heat, allowing the Earth to maintain the conditions necessary to host life, and without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the planet would be -180 degrees Celsius. The problem is that daily human activities increase the greenhouse effect, causing the planet to warm even further. One of the most important reasons behind global warming is an increase in greenhouse gases, deforestation, destruction of marine ecosystems, overpopulation. Experts agree that the industrial revolution was the tipping point when the emissions of greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere began to rise. They further state that the industrial revolution itself was caused by smaller revolutions, such as agriculture, technology, demography, transportation, finance, and the creation of a new model of production and consumption.
Firstly, it is important to be clear that climate change cannot be avoided, its effects can be mitigated and its consequences can be adapted. That is, people can combat it by implementing small- and large-scale measures that help slow down climate change. These actions are known as mitigation and adaptation measures. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the Special Report on Global Warming highlight the climate impacts of the current warming of up to 1°C as well as the risks of 1.5°C and the irreversible losses that would occur at 1°C. 2°C or more warming. We need political leadership to cut emissions immediately across the economy sectors, in order to limit warming to 1.5°C.
Track Eight Sustainable Procurement
Sustainable procurement is defined as raising awareness about the strategic importance of government procurement as a tool for achieving environmental and social sustainability goals and international commitments. The University of Baghdad adopts a strategy in this regard through:
- Sustainable procurement; i.e., energy saving procurement of energy-efficient products.
- Conversion to sustainable energy, such as: solar energy and wind energy.
- Reducing financial risks.
- Supporting people of determination, the disabled, and women without a breadwinner by purchasing their products or providing charity exhibitions in support of them.
- Reducing consumption by choosing reusable products, renting, rather than buying.
- Reducing waste generation by choosing products that can be reused and recycled.
- Avoiding products that contain toxic chemicals, especially solids.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with (GHG) product manufacturing.
University of Baghdad, Iraq
Introduction:
The University of Baghdad acknowledges the significance of integrating sustainable and socially responsible investment practices into its financial strategies. As an institution dedicated to academic excellence and global citizenship, we firmly believe that our investments should be in alignment with our core values and actively contribute to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations. This Sustainable Investment Policy delineates the principles and guidelines that will govern the University’s investment choices.
This policy underscores our commitment to responsible investment practices and underscores our dedication to creating a positive impact on both our community and the world at large. 🌍🌱📈
Principles:
- Environmental Responsibility:
– We will consider the environmental impact of our investments, aiming to support businesses and industries that demonstrate responsible environmental practices and contribute to the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Social Equity:
– Our investments will prioritize companies and projects that uphold human rights, labor standards, and diversity and inclusion principles. We will seek opportunities that foster positive social impacts within our communities.
- Governance Integrity:
– The University will invest in entities with transparent and ethical governance structures. We will actively engage with companies to promote best practices in corporate governance and accountability.
- Long-Term Sustainability:
– Investments will be evaluated with a focus on long-term sustainability, considering factors such as resource efficiency, resilience to climate change, and the ability to adapt to evolving market conditions.
- Stakeholder Engagement:
– We will actively engage with stakeholders, including students, faculty, staff, and the broader community, to ensure transparency in our investment decisions and to gather diverse perspectives on sustainability considerations.
Investment Guidelines:
- ESG Integration:
– The University will integrate ESG factors into the investment decision-making process, conducting thorough assessments of potential investments to ensure alignment with sustainability principles.
- Active Ownership:
– The University will exercise its rights as a shareholder to actively participate in decision-making processes of invested companies, advocating for sustainable practices and responsible governance.
- Divestment from High-Risk Industries:
– We will assess and, where necessary, divest from industries that pose significant environmental or social risks, such as fossil fuels, arms manufacturing, or companies with a history of human rights violations.
- Community Investment:
– The University will explore opportunities for community investment, supporting local businesses and projects that align with our sustainability goals and contribute to the well-being of the communities in which we operate.
- Regular Reporting:
– The University will provide regular reports to stakeholders on the performance of its sustainable investments, including updates on ESG considerations, engagement activities, and the overall impact on the University’s financial portfolio.
Review and Updates:
This Sustainable Investment Policy will be periodically reviewed to ensure its effectiveness and relevance. Updates may be made to reflect changes in the University’s priorities, market conditions, and best practices in sustainable investing.
By adopting this policy, the University of Baghdad affirms its commitment to responsible investing and the pursuit of a sustainable and socially conscious financial portfolio
An investment approach that integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into the investment process. The goal of sustainable investing is to generate long-term financial returns while also minimizing negative environmental and social impacts.
The university will also engage with investee companies to promote sustainable practices through a variety of channels, including:
The introduction should provide an overview of the university’s current carbon emissions and its commitment to reducing them. It should also define the terms “carbon emissions” and “net zero emissions.”
Goals and objectives
The policy should set clear goals and objectives for reducing carbon emissions. These goals should be ambitious but achievable, and they should be measurable.
Strategies and measures
The policy should outline the strategies and measures that the university will use to achieve its goals. These strategies could include:
- Investing in renewable energy sources.
- Improving energy efficiency.
- Reducing waste.
- Promoting sustainable transportation.
Monitoring and reporting
The policy should include a system for monitoring and reporting on the university’s progress in reducing carbon emissions. This system should track the university’s emissions, identify areas where emissions can be reduced, and report on the university’s progress towards its goals.
Communication and engagement
The policy should include a plan for communicating the university’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions to its students, staff, and the public. This plan should include ways to engage with these stakeholders and encourage them to take action to reduce their own carbon emissions.
Statement of Commitment
The University of Baghdad is committed to creating an inclusive and welcoming environment for all students, faculty, and staff. We believe that everyone deserves to be treated with dignity and respect, regardless of their race, ethnicity, gender, religion
Definition of Terms
For the purposes of this policy, the following terms shall have the following meanings:
Equality: The state of being equal, especially in terms of status, rights, and opportunities.
Inclusion: The act of including or making someone feel included.
Diversity: The state of being diverse, especially in terms of the variety of people and cultures represented.
Discrimination: The unjust or prejudicial treatment of a person or group on the basis of their race, ethnicity, gender, or religion.
Policies and Procedures
The University of Baghdad has a number of policies and procedures in place to promote EID. These include:
- A recruitment, hiring, promotion, and retention policy prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, ethnicity, gender, religion, or sexual orientation.
A policy on sexual harassment and discrimination that prohibits all forms of sexual harassment and discrimination. - A policy on creating a supportive and inclusive environment that outlines the university’s commitment to creating a welcoming and respectful environment for all students, faculty, and staff.
- Training and education. The University of Baghdad requires all students, faculty, and staff to complete training on EID. This training helps to raise awareness of EID issues and to promote a culture of respect and inclusion
- Reporting and accountability. The University of Baghdad has a system for reporting and investigating EID incidents. This system ensures that EID issues are addressed promptly and fairly
Bribery is the offering, giving, or receiving of anything of value in order to influence the actions of another person in a way that is improper or corrupt.
Scope of the policy
This policy applies to all employees, students, and vendors who do business with the University of Baghdad.
Prohibited Conduct
The following conduct is prohibited under this policy:
- Offering or giving a bribe to any university employee, student, or vendor.
- Receiving a bribe from any university employee, student, or vendor.
- Asking for or demanding a bribe from any university employee, student, or vendor.
- Facilitating or enabling bribery.
Reporting requirements
Any employee or other person who suspects or knows of any instance of bribery is required to report it immediately to the Office of the President.
Investigation and disciplinary procedures
All allegations of bribery will be investigated promptly and thoroughly. If an allegation is found to be credible, disciplinary action will be taken, up to and including termination of employment.
Training. All employees and other persons who are covered by this policy will be required to complete training on the policy and on the risks of bribery.
Communication
The University of Baghdad will communicate the anti-bribery policy to all employees and other persons who are covered by it. This will be done through a variety of channels, including training, posters, and newsletters.
Purpose:
The purpose of this policy is to establish standards and procedures for the use of EDI at the University of Baghdad.
Scope:
This policy applies to all departments and units of the University of Baghdad that use EDI.
Definitions:
EDI: Electronic Data Interchange is the electronic exchange of business documents between two or more organizations.
EDI standards: sets of rules that define the format and content of EDI messages.
Policy:
- The University of Baghdad will use the ANSI ASC X12 standard for EDI.
- All EDI messages must be sent and received in accordance with the ANSI ASC X12 standard.
- EDI messages must be signed and encrypted to ensure security.
- The University of Baghdad will provide training on EDI to all employees who need to use it.
Responsibilities:
The EDI Coordinator is responsible for the implementation and management of EDI at the University of Baghdad.
All departments and units that use EDI are responsible for ensuring that their employees are trained on EDI and that they comply with the EDI standards.
Enforcement:
Violations of this policy may result in disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment.
This policy is effective immediately.
Additional Information:
The University of Baghdad has an EDI Coordinator who can provide more information about this policy and the implementation of EDI at the University.
The University of Baghdad has a website with resources on EDI, including the ANSI ASC X12 standard and training materials.
Purpose
The purpose of this policy is to create a workplace free from harassment. Harassment is any unwelcome conduct that is based on a person’s sex, race, religion, national origin, age, disability, or other protected characteristic. It can include verbal, physical, or visual conduct.
Scope
This policy applies to all employees, students, and visitors of the University of Baghdad.
Definitions
Harassment: any unwelcome conduct that is based on a person’s sex, race, religion, national origin, age, disability, or other protected characteristic. It can include verbal, physical, or visual conduct.
Retaliation: any adverse action taken against a person who has made a complaint of harassment or who has participated in an investigation of a complaint of harassment.
Policy
The University of Baghdad is committed to creating a workplace free from harassment. All employees, students, and visitors are expected to abide by this policy.
The following are examples of prohibited conduct:
- Verbal conduct: This includes making offensive or derogatory comments, jokes, or remarks about a person's sex, race, religion, national origin, age, disability, or other protected characteristic.
- Physical conduct: This includes touching, grabbing, or other physical contact that is not welcome.
- Visual conduct: This includes displaying or distributing offensive or derogatory images or cartoons.
Reporting Harassment
If you believe that you have been harassed, you should report the incident to your supervisor, the Human Resources Department, or the Title IX Coordinator. You can also report the incident to the police.
When you report an incident of harassment, you will be asked to provide information about the incident, including the date, time, and location of the incident, the names of the people involved, and a description of the conduct.
The University of Baghdad will investigate all complaints of harassment promptly and thoroughly. If the investigation finds that harassment has occurred, the University will take appropriate action, up to and including termination of employment.
Retaliation
The University of Baghdad will not tolerate retaliation against anyone who reports harassment or who participates in an investigation of a complaint of harassment. If you believe that you have been retaliated against, you should report the incident to your supervisor, the Human Resources Department, or the Title IX Coordinator.
Enforcement
Violations of this policy may result in disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment.
University of Baghdad’s Donation Policy
University of Baghdad, Iraq
Introduction:
The University of Baghdad, as a public institution dedicated to academic excellence and community development, acknowledges the significance of sustainable donations and funding in advancing its mission and objectives. This Sustainable Donations/Funding Policy delineates the principles and guidelines that will govern the acceptance of donations and funding, ensuring alignment with the University’s core values and unwavering commitment to sustainability.
This policy underscores our commitment to responsible financial practices and reinforces our dedication to creating a positive impact on both our community and the world at large. 🌍🌱💙
Principles:
1.Mission Alignment:
– The University will prioritize donations and funding that align with its educational mission, values, and commitment to serving the public good.
- Sustainability Criteria:
– Donations and funding will be assessed based on their sustainability impact, considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Preference will be given to contributions that promote sustainable practices and positive community outcomes.
- Transparency and Accountability:
– The University will maintain transparency in its fundraising activities, providing clear information about the purpose and use of donations. Accountability mechanisms will be in place to ensure responsible stewardship of funds.
- Avoidance of Conflicts of Interest:
– The University will take steps to avoid conflicts of interest in donation acceptance. Contributions that may compromise the integrity and independence of the institution will be carefully reviewed and, if necessary, declined.
- Community Engagement:
– The University will actively engage with its community, including students, faculty, staff, and the broader public, to gather input on donation considerations. Community feedback will be considered in decision-making processes.
Guidelines for Acceptance:
- Ethical Sources:
– The University will accept donations and funding only from ethical sources, avoiding contributions from entities engaged in activities that contradict the University’s values or violate human rights.
- Compliance with Laws and Regulations:
– Donations will comply with all applicable laws and regulations. The University will conduct due diligence to ensure that accepted funds do not violate legal or ethical standards.
- Non-Discrimination:
– The University will not accept donations that discriminate against any individual or group based on race, gender, religion, ethnicity, or any other protected characteristic.
- Environmental Responsibility:
– Donations will be evaluated for their environmental impact, and preference will be given to contributions that support sustainable practices and align with the University’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
Stewardship and Reporting:
- Responsible Stewardship:
– The University will manage donations and funding responsibly, ensuring that they are utilized for their intended purposes and in a manner consistent with the institution’s values and goals.
- Regular Reporting:
– The University will provide regular reports to stakeholders on the utilization of donations and funding, demonstrating transparency and accountability in financial matters.
Review and Updates:
This Sustainable Donations/Funding Policy will be periodically reviewed to ensure its effectiveness and relevance. Updates may be made to reflect changes in the University’s priorities, regulatory landscape, and best practices in sustainable fundraising.
By adopting this policy, the University of Baghdad affirms its commitment to ethical and sustainable fundraising practices in support of its public service mission.
Welcome to EcoHarmony Baghdad: Fostering Sustainability through Innovation
About Us: EcoHarmony Baghdad is a dynamic student organization proudly managed by the College of Engineering at the University of Baghdad. Our mission is to promote environmental sustainability through innovative projects, research initiatives, and community engagement. We are dedicated to inspiring positive change and fostering a sense of responsibility towards our planet.
Our Vision: To become a catalyst for sustainable practices within our university community and beyond, driving positive environmental impact through collaboration, research, and awareness.
Objectives:
- Innovative Projects: We initiate and implement sustainable projects that address environmental challenges and contribute to the well-being of our community.
- Research Excellence: We are committed to advancing knowledge in environmental sustainability. Our organization has published numerous papers detailing our projects, findings, and solutions.
- Community Engagement: EcoHarmony Baghdad actively engages with the local community to raise awareness about environmental issues and promote sustainable practices.
- Education and Outreach: We organize workshops, seminars, and events to educate our peers and the public on the importance of environmental sustainability and how they can contribute.
Publications: Explore our library of research papers and publications covering a wide range of topics related to environmental sustainability. Our organization is proud to have contributed valuable insights to the academic community and beyond.
Sample of Publication:
- Shukur, S. A., Hassan, F. M., & Fakhry, S. S. (2024). Unveiling the Nexus the link between water quality index and phthalic acid ester concentrations in Tigris River. Emerging Contaminants, 10(1), 100279.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2023.100279
- Wahhab, T. A., & Hassan, F. M. Change in Hydro-Chemical Properties and Water Quality of a Lentic Eco-systems: Baghdad Touristic Island Lake.
http://dx.doi.org/10.21931/RB/CSS/2023.08.04.06
- Abdulateef, M. F., & Al-Alwan, H. A. (2023, March). Definition of streets priority to employ urban green infrastructure in Baghdad City. In AIP Conference Proceedings(Vol. 2651, No. 1). AIP Publishing.
https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0105900
- Abdulateef, M. F., & Al-Alwan, H. A. (2022). Planning Steps of Urban Green Infrastructure in Existing Cities. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum Administratio Locorum, 21(4), 465-478.
https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1094743
- Abdulateef, M. F., & Al-Alwan, H. A. (2022). The effectiveness of urban green infrastructure in reducing surface urban heat island. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 13(1), 101526.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2021.06.012
- Fazaa, N. A., Ali, A. B., AL-Jabinawi, A. J., Francksen, R., & Whittingham, M. J. (2022). Land use change in Baghdad City and assessment of the Jadriyah and Umm Al-Khanazeer Island Important Bird Area (IBA) from 1984 to 2020. Baghdad Science Journal, 19(6 (Suppl.)), 1471-1471.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21123/bsj.2022.7033
- Ghayyib, M. N., Al-Rubaie, A. I. F., & Adnan, F. A. (2023, July). A Statistical Analysis of the Effects of Afforestation on the Environment in Iraq (Northern Iraq). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science(Vol. 1215, No. 1, p. 012039). IOP Publishing.
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/1215/1/012039/meta
- Abdel-Hussein, M. A. R., & Fayyadh, S. O. (2023, November). Requirements for Developing the Technical Capabilities of Agricultural Extension Service Providers to Face the Effects of Climate Change in Baghdad Province. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science(Vol. 1259, No. 1, p. 012131). IOP Publishing.
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/1259/1/012131/meta
Get Involved: Whether you are a student, faculty member, or passionate individual, there are various ways to get involved with EcoHarmony Baghdad. Attend our events, participate in projects, or collaborate on research initiatives – your contribution matters!
Contact Us: Connect with us to learn more about our organization, upcoming events, or if you’re interested in collaborating. Your ideas and enthusiasm are always welcome!
Follow Us: Stay updated on our latest projects, events, and news by following us on social media. Join the conversation and be part of the movement towards a more sustainable future.
EcoHarmony Baghdad is not just an organization; it’s a community united by a common goal – creating a sustainable and harmonious environment for generations to come. Join us in making a difference!
